Understanding and Investing Market Volatility (CBOE VIX Index)
What is the VIX Index?
The Chicago Board Options Exchange Volatility index - better known as the VIX or fear index- is a calculation designed to produce a measure of constant, 30-day expected volatility of the U.S. stock market, derived from real-time, mid-quote prices of S&P 500® Index (SPX) call and put options. Globally, the VIX is one of the most recognised measures of volatility and provides all investors a clear picture of US stock market conditions and market uncertainty.
Historical VIX trends & VIX & S&P500 Correlation
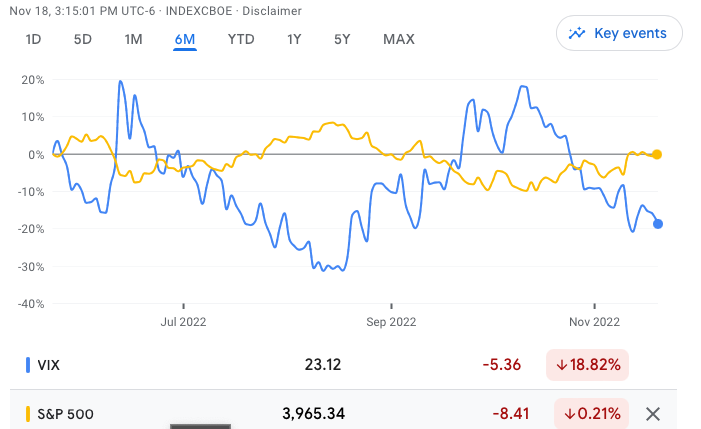
The below comparison (Chart 2) between the S&P 500 & the VIX over a 6 month period illustrates a spike in the VIX during negative S&P 500 performance. As mentioned above, major market disruptions such as; global financial crisis 2008; COVID pandemic 2020; European sovereign debt crisis 2011 have all resulted in huge spikes in the VIX. So the question is, how can investors successfully trade the VIX?
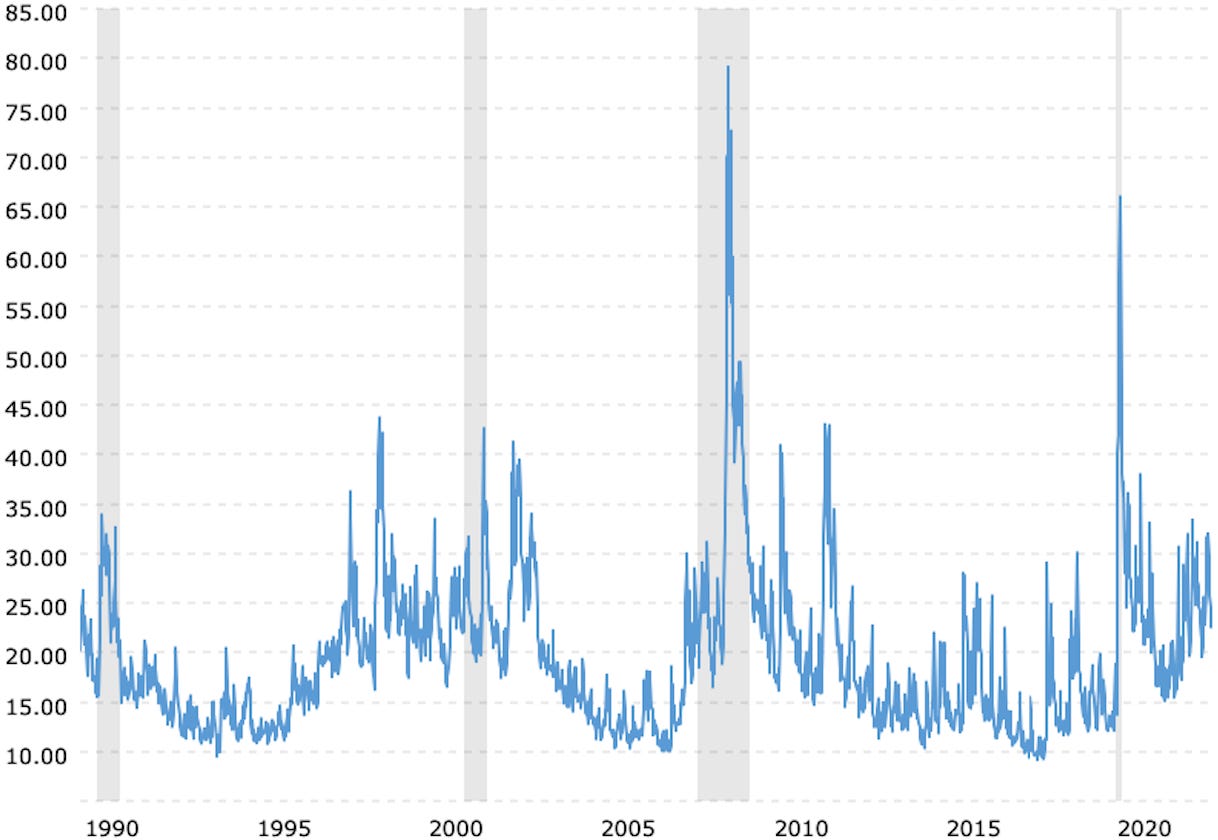
Historically, we know the VIX index all time low (support level) is 9.14 (2017) and typically during bullish stock market conditions, the VIX averages 10-20, implying low market volatility. Investors can use these support levels to buy VIX low and sell high. Generally speaking, buying low, near these support levels can provide protection as we know historically the VIX won’t drop below these levels, making this an attractive investment on a cyclical basis. Support levels further indicate market tops and warn of a potential downturn in the S&P 500.
In addition, when the VIX reaches resistance levels, it is considered high and is a signal to purchase stocks—particularly S&P 500 stocks or index linked mutual funds. Spike in the VIX indicates market uncertainty and poor S&P performance, providing investors with a potential, ‘buy the dip’ approach.
A quick analysis of the below charts show that the VIX bounces between a range of approximately 18-35 the majority of the time but has outliers as low as 10 and as high as 85. Despite these trends, the VIX always reverts back to the mean. Understanding these trends is helpful for investors to make better decisions. Even after the harsh bearishness of 2008-2009 and COVID pandemic in 2020, the VIX moved back within its normal range.
Chart 1 - VIX all time performance
Chart 2 - S&P 500 (Bellow) & VIX (Blue) 6 month performance
How can I invest in the VIX?
The VIX can be traded through futures contracts and exchange traded funds (ETFs) and exchange traded notes (ETNs) that own these futures contracts. These are the three ways you can invest in the VIX:
Futures - available to invest via institutional brokerage services - not for retail investors
Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) - An ETF is a type of pooled investment security which is publicly listed on a stock exchange. Typically, ETFs will track a particular index, sector, commodity, or other assets. VIX ETF’s seek to offer exposure to market volatility by holding short/mid term VIX futures contracts to maturity- short term 30 days/mid term 5 months.
ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF (VIXM) 32.33 USD
ProShares Short VIX Short-Term Futures ETF (SVXY) 54.76 USD
Exchange Traded Notes (ETN) - An ETN is more like a bond. It's an unsecured debt note issued by an institution. ETN’S can be held to maturity or traded OTC. If the underwriter (financial institution) were to go bankrupt, the investor would absorb the risk. VIX ETN’s are designed to track the value of futures contracts on Cboe Volatility Index, which is a gauge of current volatility that is priced into S&P 500 index options.
iPath Series B S&P 500 VIX Short-Term Futures ETN (VXX) 16.41 USD
iPath® Series B S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Future ETN (VXZ) 27.54 USD
Online Trading platforms
Etoro
IG Group
Interactive Investor
Plus500